Solution
This chapter is non-technical, suited to explain the concepts. The next chapter will dive into technical design.
What is Axone?
Axone has been purposefully structured as a custom blockchain to ignite a new wave of innovation based on shared digital resources. Its aim is to provide a unique solution to the challenges inherent in digital resource sharing while enabling the orchestration of various shared resources.
Axone facilitates interoperation among resources while ensuring constant adherence to associated consent rules and continuous auditability. This capability positions Axone as an innovative player in the digital landscape, providing a trustworthy and efficient solution to the complex issues of resource sharing in the digital era.
How Axone solves the sharing issues?
TRUST
Axone leverages blockchain technology to cultivate trust in the ecosystem, both for providers and consumers of data and digital services. By building on the trustless nature of the public blockchain, Axone eliminates the need for third-party intermediaries as a source of trust, minimizing risks of bias or mismanagement. The decentralized nature of the protocol ensures transparency and impartiality, allowing anyone to independently verify transactions and adherence to consent and sharing rules.
For providers, this guarantees that their specified conditions for sharing will be respected, building trust and encouraging a more open sharing of digital resources. For consumers, the trustless and transparent nature of the blockchain offers assurance that they are accessing legitimate services, adhering to the agreed terms, and that their transactions are secure and verifiable. Furthermore, it provides them with the confidence to interact with a multitude of providers in the ecosystem, knowing that the terms of engagement are transparent, fair, and enforceable.
In this way, Axone fosters a climate of trust that benefits all stakeholders in the ecosystem and promotes a more collaborative and knowledge-rich digital landscape.
INCENTIVES
Recognizing the integral role that incentives play in motivating participants to share data and knowledge, Axone provides an innovative and highly flexible system for compensation and business models. The protocol is designed to allow anyone to establish their own conditions and prices. It could include designing their compensation models and creating applications with their own tokenomics based on shared resources.
The flexibility inherent in Axone extends beyond economic models to include rules of consent. The protocol's high degree of customization enables participants to set their own terms for sharing, respecting individual interests and encouraging more open sharing of digital resources. This ability to control how, when, and under what terms data and services are shared offers providers greater sovereignty over their resources, fostering the knowledge creation.
Furthermore, Axone reduces complexity by serving as a minimally extractive coordinator, facilitating interactions between providers and users of digital resources. By acting as a neutral and efficient intermediary, Axone reduces the costs and difficulties associated with data sharing. It provides an accessible and standardized interface that reduces the technical complexities of interacting with diverse datasets and digital services.
From a consumer perspective, the openness encouraged by Axone fosters collaboration and competition, leading to a more dynamic and innovative digital landscape. This environment, combined with reduced costs due to the elimination of intermediaries, provides a more equitable value proposition for consumers.
FRAGMENTATION
Axone tackles the challenge of fragmentation by offering a solution that enables 'Anything as a Service'. This approach significantly reduces friction and fragmentation, thereby fostering a more varied and cohesive digital ecosystem. By empowering any digital resource to be offered as a service, Axone dismantles the barriers of isolated data silos. It enhances resource discoverability and utilization across various sources and formats, ultimately stimulating the generation of new and valuable knowledge.
The protocol's interoperability plays a vital role in addressing technical fragmentation. As a technology-agnostic solution, Axone enables seamless interaction between diverse systems, platforms, and technologies. It transcends the boundaries between the Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 ecosystems, ensuring that all digital resources can be effectively shared and utilized. This flexible and inclusive approach drives knowledge creation and stimulates innovation, promoting a more collaborative and efficient digital landscape.
In addition to addressing technical fragmentation, Axone also provides a comprehensive and expressive representation of different digital resources and their interactions. Given the wide variety of datasets and services, recording resources and their interactions is not sufficient ; it's necessary to understand and interpret the characteristics of a resource and its relationships with others. Axone's expressive formal representation allows for efficient comprehension and coordination among diverse resources, enhancing their utilization and the generation of valuable insights.
Protocol Overview
How does Axone work?
Axone leverages the referenced resources into the protocol to construct digital commons, termed zones, where digital resources can be shared and orchestrated to create knowledge. To each zone and shared resource is attached customizable rules concerning every facet of resource sharing. This includes aspects such as access control, data and service management, business models, governance frameworks for instance. The Axone protocol ensures proper compliance with the rules and the execution.
Zone overview
The primary objective of zones is to facilitate the coordination of heterogeneous systems and resources. Zones aim to integrate all systems, both on-chain and off-chain.
What is a zone ? A zone is a conceptual framework defined by a set of rules, within which the recognized digital resources are compatible with these rules, taking into account the associated consents. Thus, the recognition of resources within a zone relies on the dynamic evaluation of the conformity of the rules and consents of the resources.
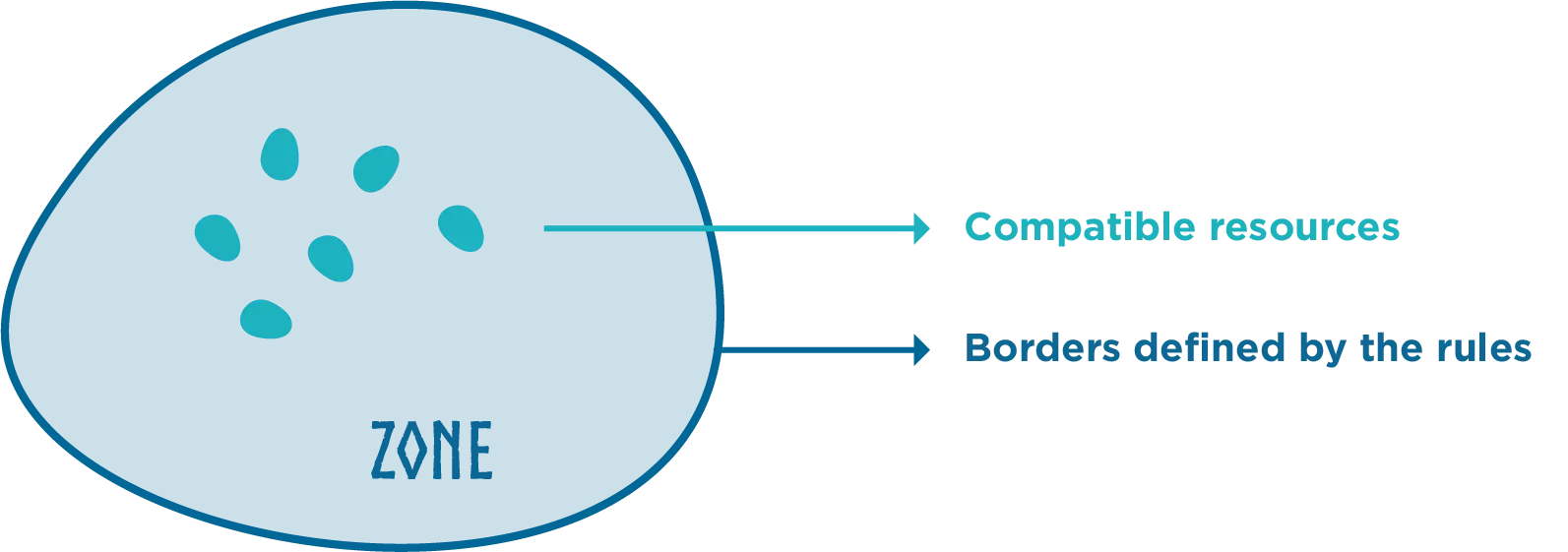
Another way to perceive it is through the rules of the zone which can be either open or on the contrary restrictive . The existence of these rules defines the reality of the zone, and it is through the consideration (evaluation) of digital resources that are compatible with the zone that the extent of the zone's territory is defined. In other words, the rules establish the boundaries and parameters that determine which digital resources fall within the zone and are recognized as part of it. By evaluating the compatibility of resources with the zone's rules, the scope and coverage of the zone can be determined. Multiple zones may share common resources and can be nested or overlapped, based on the rules associated with each resource and zone.
There is then an endless combination of oftentimes interoperable zones where participants and digital resources can interact freely and create value.
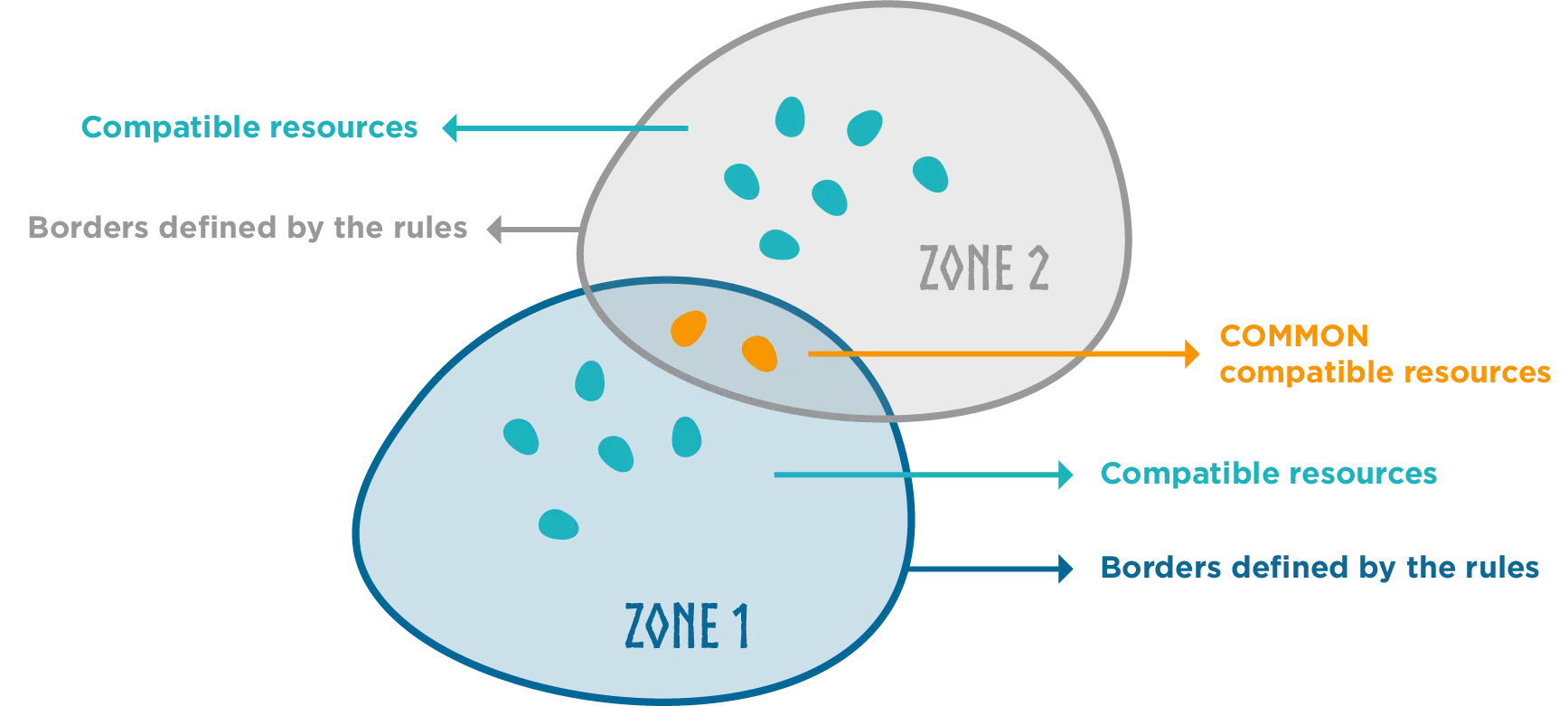
Why no direct link between zone and resources? If there is no materialized link determining the belonging of a resource to a zone, it is because zones are designed to constantly evolve through their rules and conditions which continuously redefine their boundaries.
The Dataverse
The Dataverse is an ever-expanding universe comprised of all the digital resources, such as datasets, and digital services such as infrastructure services, processing services or any other digital service referenced in the Axone Blockchain.
All resources, services and zones are found within the same universe, the Dataverse.
Zones can be nested and overlapping, as one resource or service can participate in many zones, and many applications can be built on top of one zone. The whole is greater than the sum of its parts: this is the Dataverse.
What's the purpose ? Creating a general purpose Ecosystem that enables XaaS integration Anything that is presented to the Protocol as a Service, whatever it does, wherever it is hosted or deployed (in the cloud or on premise), whoever provides it, it can be used by the Protocol. Therein lies the integration power of the protocol, which brings infinite scalability and extensibility to the entire Axone ecosystem. The description of each resource referenced in the protocol ensures their proper processing by the different entities of the protocol.
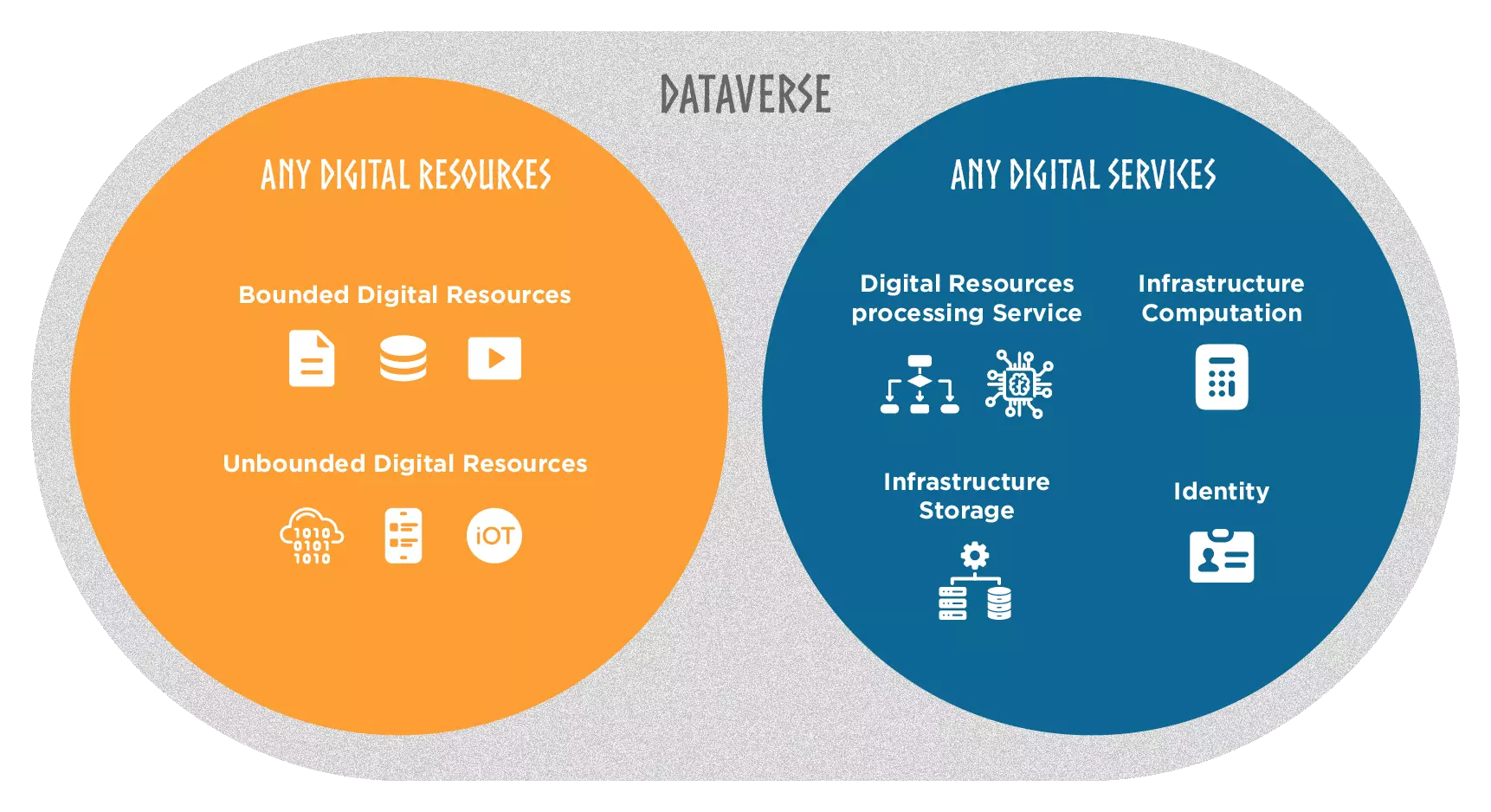
There are two main categories of resources in the dataverse:
- Digital Resource
- Digital Service
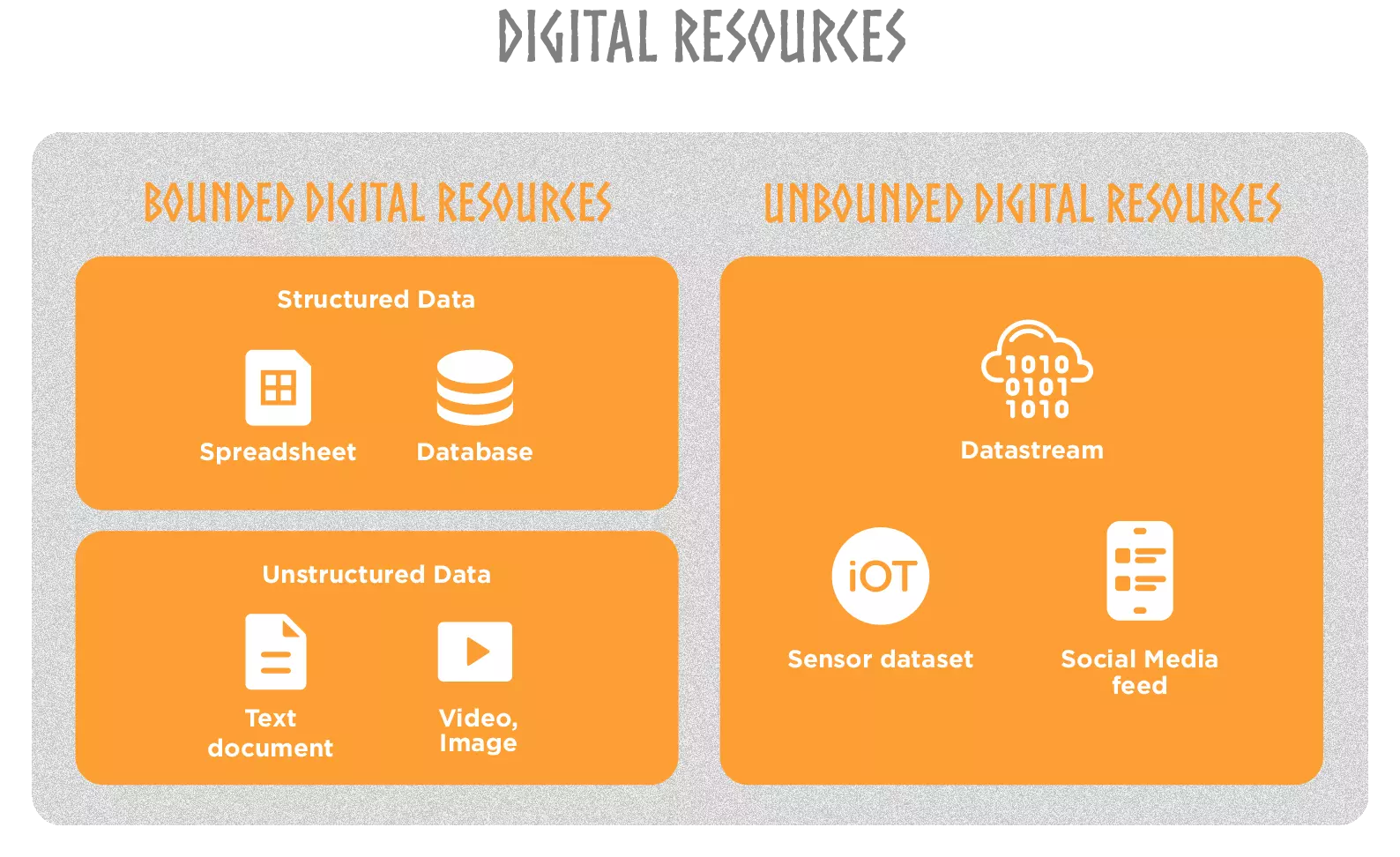
Digital Resources encompass various forms of data and information, which can be expressed, carried and stored in different formats. They serve as the raw material from which insights and new knowledge are derived. These resources can be classified into different categories, we can summarize here:
- Bounded Digital Resources which have a finite size and are often accessed and analyzed as a whole. We call them datasets, and can be classified into structured data, such as databases or spreadsheets, and unstructured data, such as text documents, images, or videos, to name a few.
- Unbounded Digital Resources, such as data streams, are characterized by their continuous and potentially infinite nature. They involve a continuous flow of data that is generated over time, often in real-time or near real-time. Examples of unbounded resources include sensor data from IOT, social media feeds, or stock market tickers, to name a few.
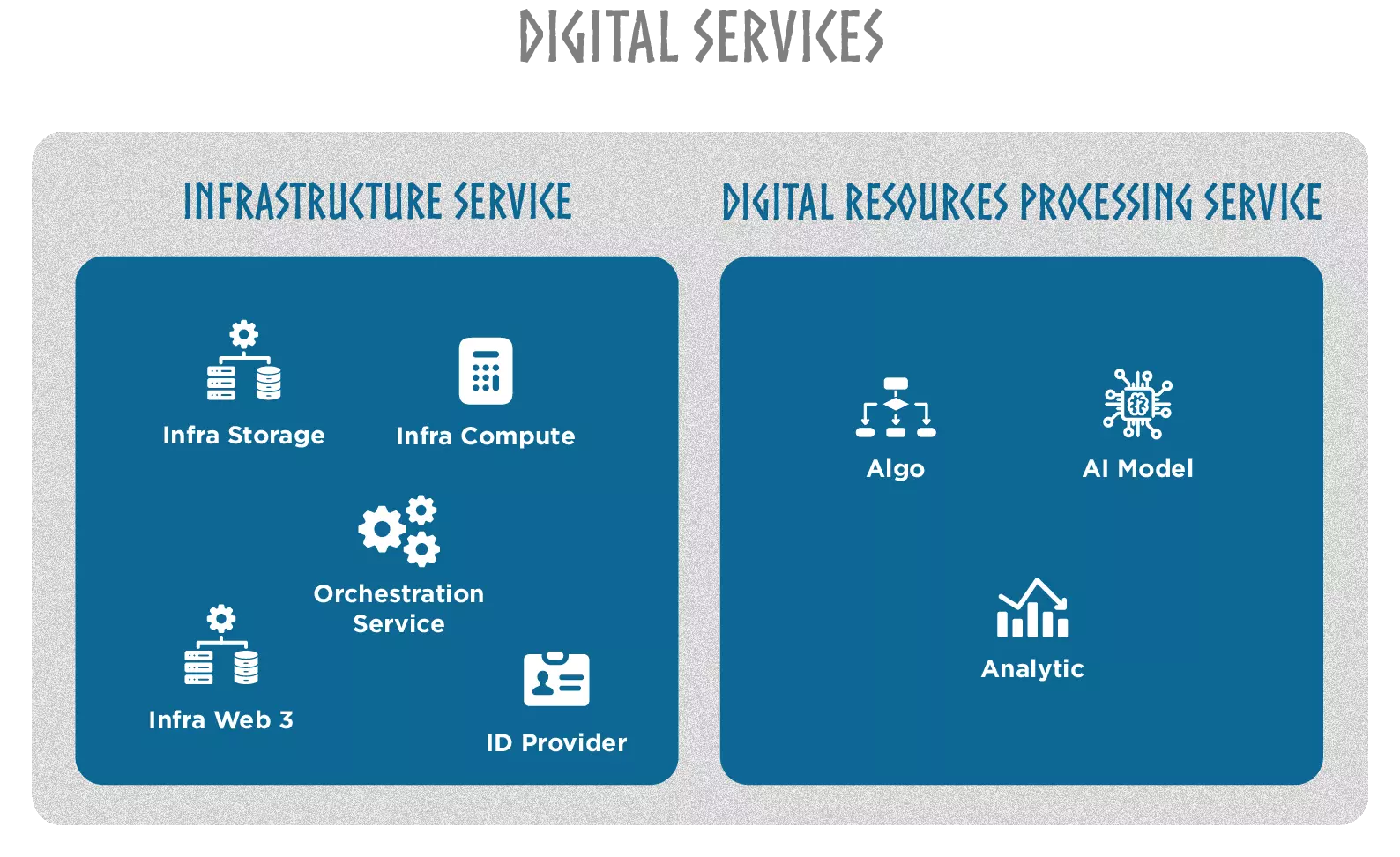
Digital Services, on the other hand, are essential components that handle and support the transformation of these digital resources into actionable knowledge. From this perspective, Digital Services serve as the structural and functional unit in the process of Knowledge creation. They provide the necessary means to transform the digital resources, enabling the generation of new knowledge. Digital Service includes:
- Infrastructure service
- Digital resource processing Service
STaaS-Storage as a service: The Dataverse is capable of supporting all storage options. These range from local storage options to cloud storage solutions operated by major providers such as Dropbox or AnyDrive. Additionally, decentralized storage networks like InterPlanetary File System (IPFS), Filecoin, or Arweave can also be integrated into the platform.
Compute-as-a-Service: Similarly, the Dataverse is adaptable to a range of computation options. While many services will be provided as APIs with their own computational resources, others can be executed on cloud services operated by commercial entities or decentralized compute resources. This flexibility is essential for accommodating different types of computational tasks and workloads. Relevant general purpose compute networks as Akash can be easily referenced into the protocol.
Identity Provider: In terms of identity management, the Dataverse can integrate with various identity management services or identity standards, depending on the specific requirements. Whether it's a simple, a decentralized identity management system, or a more complex centralized identity service, Axone can support it, providing secure and flexible solutions for identity management;
Orchestration-as-a-Service: The Orchestration Service is a crucial service of the Protocol which orchestrates the invocations of other services. It is a reflex component of the Ecosystem that listens to the transactions of the blockchain and is triggered on command, when a particular transaction of execution request is registered in the blockchain. It's important to note that, given the potential for multiple instances of the service and several types of orchestration services, there is a decentralized mechanism in place that ensures the correct instance of the appropriate type is executed.
Algorithms and Models: From simple logical rules to sophisticated AI-driven algorithms, machine learning models, data processing scripts, image recognition models, predictive analytics, natural language processing (NLP) models, and even blockchain smart contracts, the Dataverse is designed to accommodate and utilize a diverse range of algorithms and models. Their inclusion is dictated solely by the unique needs and objectives of the tasks at hand.
Analytic-as-a-Service: In an era of increasing data complexity and volume, effective knowledge representation is pivotal. The Analytics and Business Intelligence services is designed to transform raw data into useful insights, employing tools of B.I and Knowledge Graphs. BI tools can be effectively employed to comprehend the data shared within the zones and facilitate the extraction of useful knowledge. Knowledge Graph can facilitate the interpretation of the complex interactions and dependencies within the Dataverse, offering an intuitive view of the knowledge extraction processes.
Ontology
Given that resources are not directly attached to a specific zone, but rather deemed compatible with certain zones based on their rules and conditions, it is crucial for the Axone protocol to accurately represent and interpret these diverse concepts within its framework. Furthermore, the protocol must efficiently distinguish and understand various consent rules, their dependencies, and hierarchies. Consequently, the protocol has to express as clearly as possible the context, the meaning of the concepts and their relationships.
To really leverage the power of knowledge, Axone protocol interprets all these entities and concept within a universal language taking into account the semantic aspect of each of them. Let's take an illustration to clearly understand.
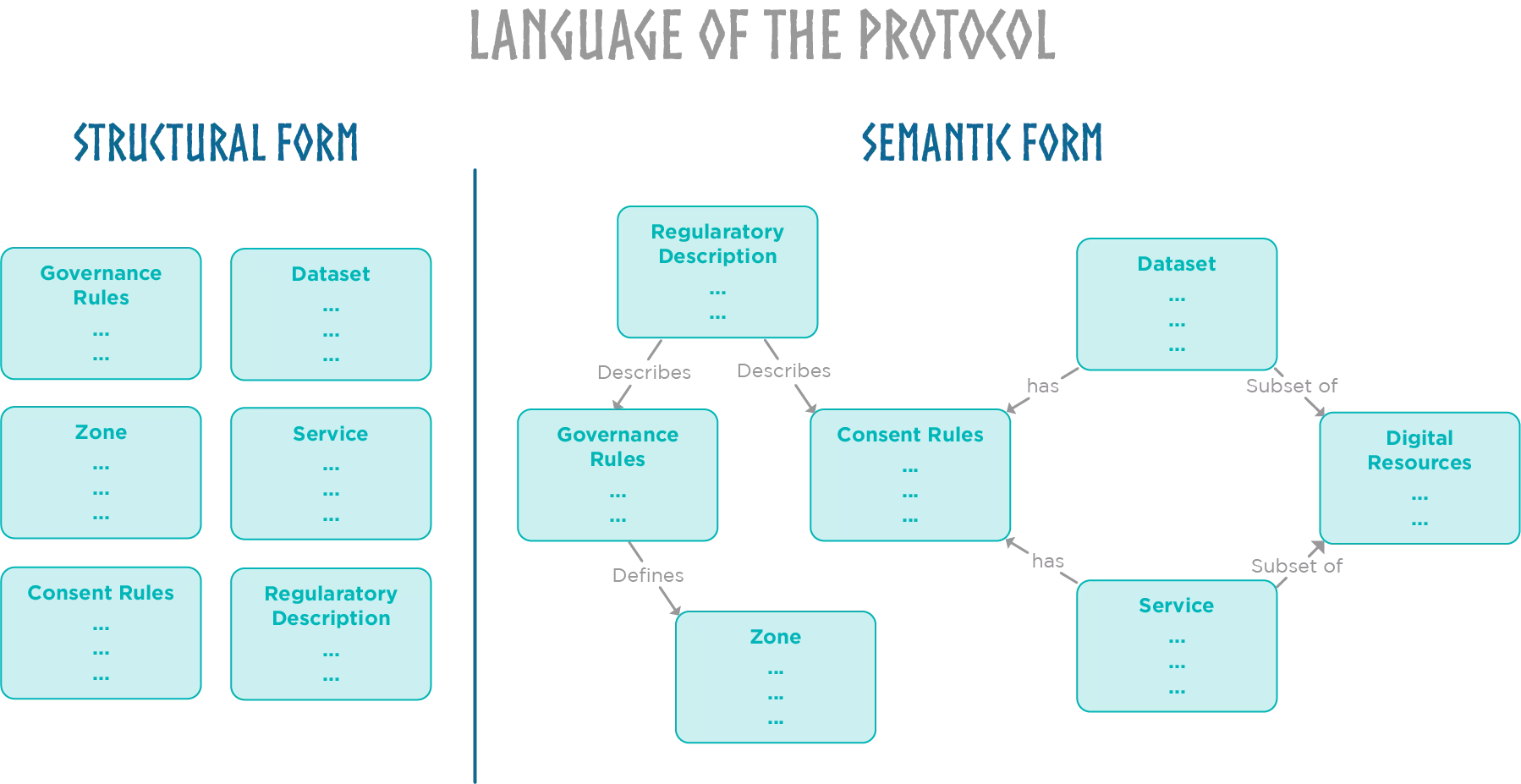
The structural language only gives a definition of concepts in a wide range. However, the semantic language could give the meaning of concepts, properties, relationships and entities. The expressiveness of the language enhances the disambiguation and the interoperability between entities in a computable form. To give meaning to each concept and entity in the protocol, we've decided to encode an ontology to represent and persist the information on the blockchain.
Ontology overview: In a broader, philosophical context, ontology is concerned with the nature of being, structuring a system of universal categories and their intrinsic relationships to explain existence itself. In computer science, an ontology is an explicit, formal representation of knowledge in a particular domain. It serves as a kind of map or guide, defining key concepts and the relationships between them.
In the context of the Axone protocol, our ontology serves to model a semantic network of all entities—such as zones, data, services, rules, processing workflows, and more—by defining what they are and how they relate to each other. The Axone ontology is stored on-chain as a smart contract, called Cognitarium. Storing the ontology on-chain guarantees the protocol's expressiveness and facilitates its structured understanding.
What are the benefits for Axone Protocol? Storing ontology on the blockchain and leveraging it to imbue resources and datasets with meaning carries significant implications for both execution and verification.
Execution: The benefits of an ontology extend to both execution and interpretability. An ontology, acting as a shared semantic framework, enables standardization and interoperability among resources. This makes it easier for diverse resources to connect and collaborate. In addition, an ontology provides a comprehensive understanding of resources within a zone and their applicable governance rules. By delivering a clear data lineage, it ensures each piece of data is traceable through various treatments
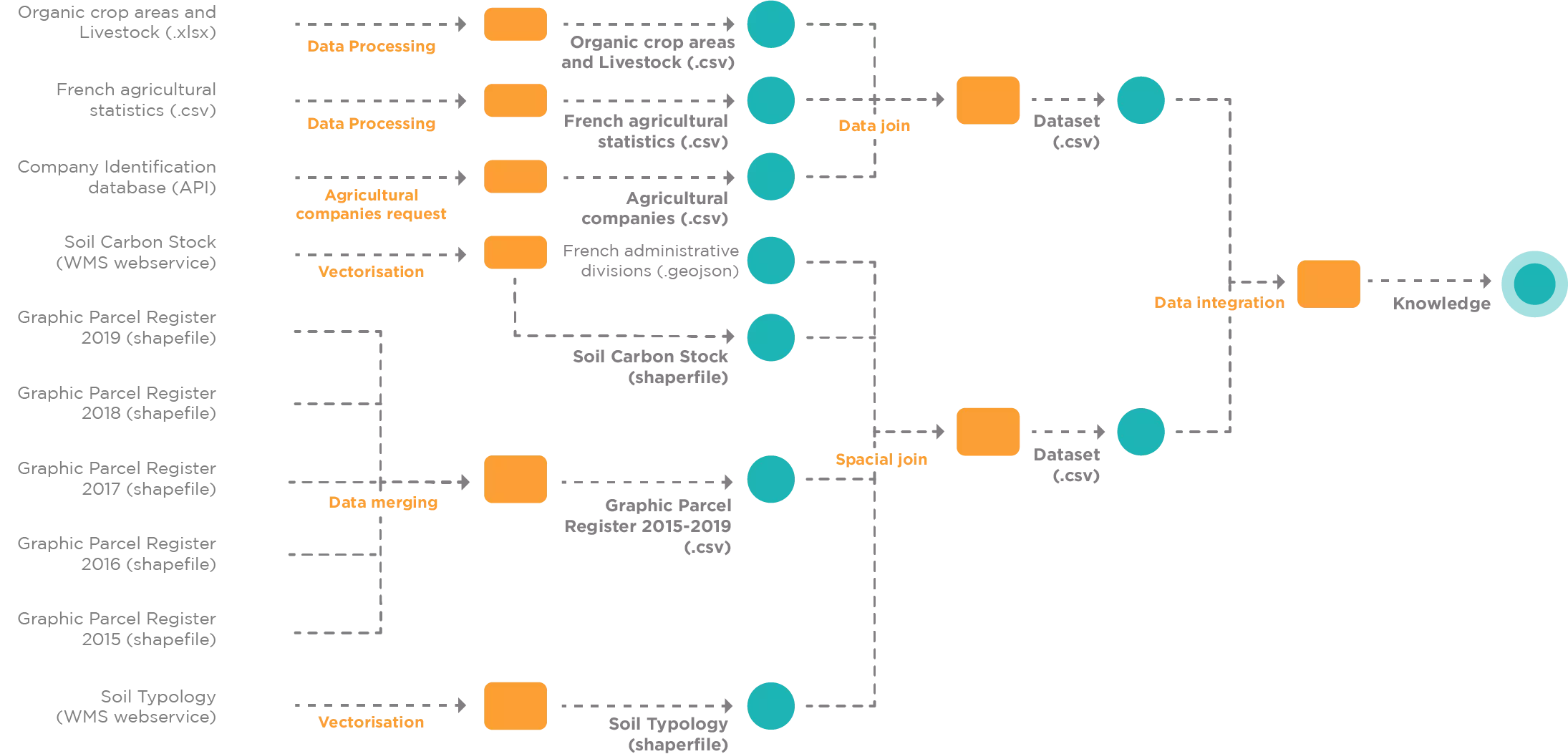
Interpretability & Representation: Ontology also provides a comprehensive and dynamic understanding of datasets within a zone, their transformation (by services), and the applicable governance rules (data sharing, consents, policy rules). From this perspective, it delivers the data lineage (enabling traceability) for each piece of data within the zones during various treatments, culminating in a knowledge graph of all used resources within the Dataverse. In addition to serving as an immutable source of truth, the blockchain will provide detailed insight into the knowledge generation process, thereby qualifying itself as an interpretable settlement layer.
Below, an example of a workflow representation in the form of a knowledge graph, generated thanks to the information stored on-chain.
PROTOCOL FUNCTIONALITY
Having established the various entities within the Axone protocol - zones, resources, consent rules, governance rules, and others - it is clear that the protocol is capable of accurately representing and interpreting these diverse elements. Now, it's time to explore the functionality of the protocol, specifically the features that allow users to leverage its unique design to their advantage.
Share any resources
As an agnostic and interoperable infrastructure, Axone enables the sharing of any type of digital resource. Within the Axone protocol, sharing does not mean giving away or transferring ownership of a resource. Instead, it's about referencing a resource within the protocol, with specific rules governing its use. So, when we talk about sharing, it doesn't mean providers lose control of their resources. They can set rules and conditions that suit their needs. Furthermore, to facilitate resource sharing and encourage collaboration among diverse entities, Axone provides open-source, no-code interfaces that simplify and streamline the resource referencing process, making it frictionless and straightforward.
Define and enforce any customized rules on-chain
One of the primary functions of the Axone protocol is to facilitate a broad spectrum of governance and consent rules. However, with a wealth of digital resources, each with their own rules, the combination of multiple resources can lead to complex logical scenarios. Here's how it works in practice: a user wants to interact with a zone, and the zone refers to the protocol's rules to determine if the user's action is permitted. This takes into account the context at the time of the request, as the rules and digital resources registered in the blockchain are continuously evolving. From a computer science perspective, the challenge lies in resolving occasionally complex logical problems among the different rules. This includes notions of hierarchy, inconsistency, dependency, and conflict resolution in terms of access, etc.
To tackle this, Axone aims at providing a reliable and secure mechanism to ensure that all the invoked rules are correctly interpreted in a decentralized way. Each zone's established rules determine whether a user's intended action is permissible or not. It's essential to note that these considerations must also account for the different contexts at the time of the request, as the state of the blockchain evolves.
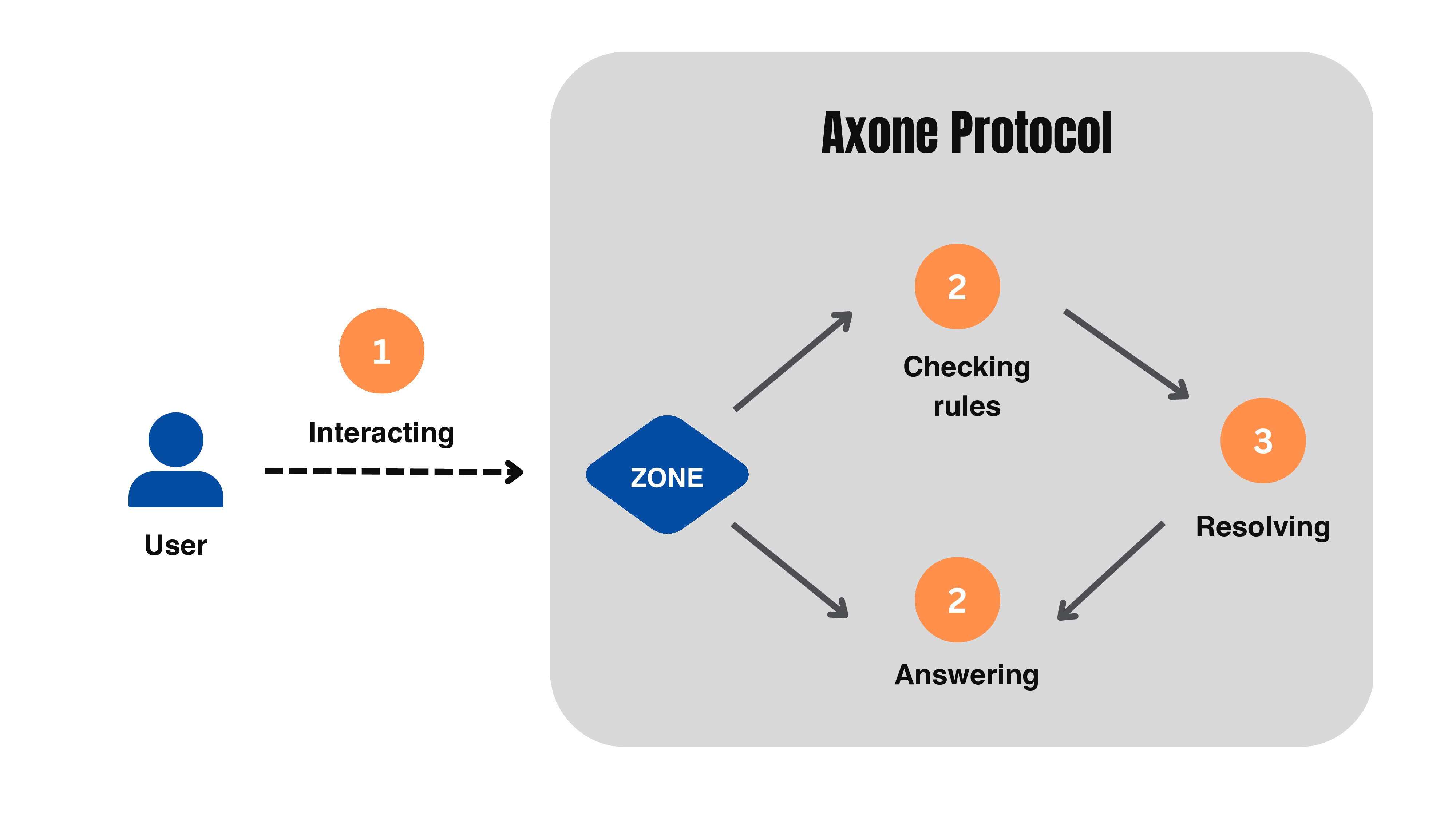
- An Identity (human or bot) wants to interact with a zone
- The zone asks the dedicated smart contract if it's possible given the context and all the involved rules
- The protocol employs logical inference to resolve matters based on the state of the blockchain
- The protocol yields a modality as a response, such as "prohibited", "permitted", "possible", and so on. Depending on the answer, the execution process could start.
Orchestrate the resources according to the rules
Execution refers to the process of orchestrating resources and executing the workflow to generate knowledge. The Axone Protocol orchestrates the execution of the workflow in a decentralized manner. This presents a significant challenge due to the many connections, interactions, and dependencies that exist in both on-chain and off-chain environments.
The challenge here is to ensure that all the events of the protocol are executed in a reliable environment so that all parties involved see their conditions respected with a trust minimized process and they are able to follow the workflow progress. A Service Execution Agreement in the form of a smart contract called PACTUM outlines the terms of the agreement that binds the stakeholders together - the consumer and providers. It does not execute the workflows itself, but rather ensures their composability and integrity by clearly defining the contractual terms.
How does the Pactum smart contract work?
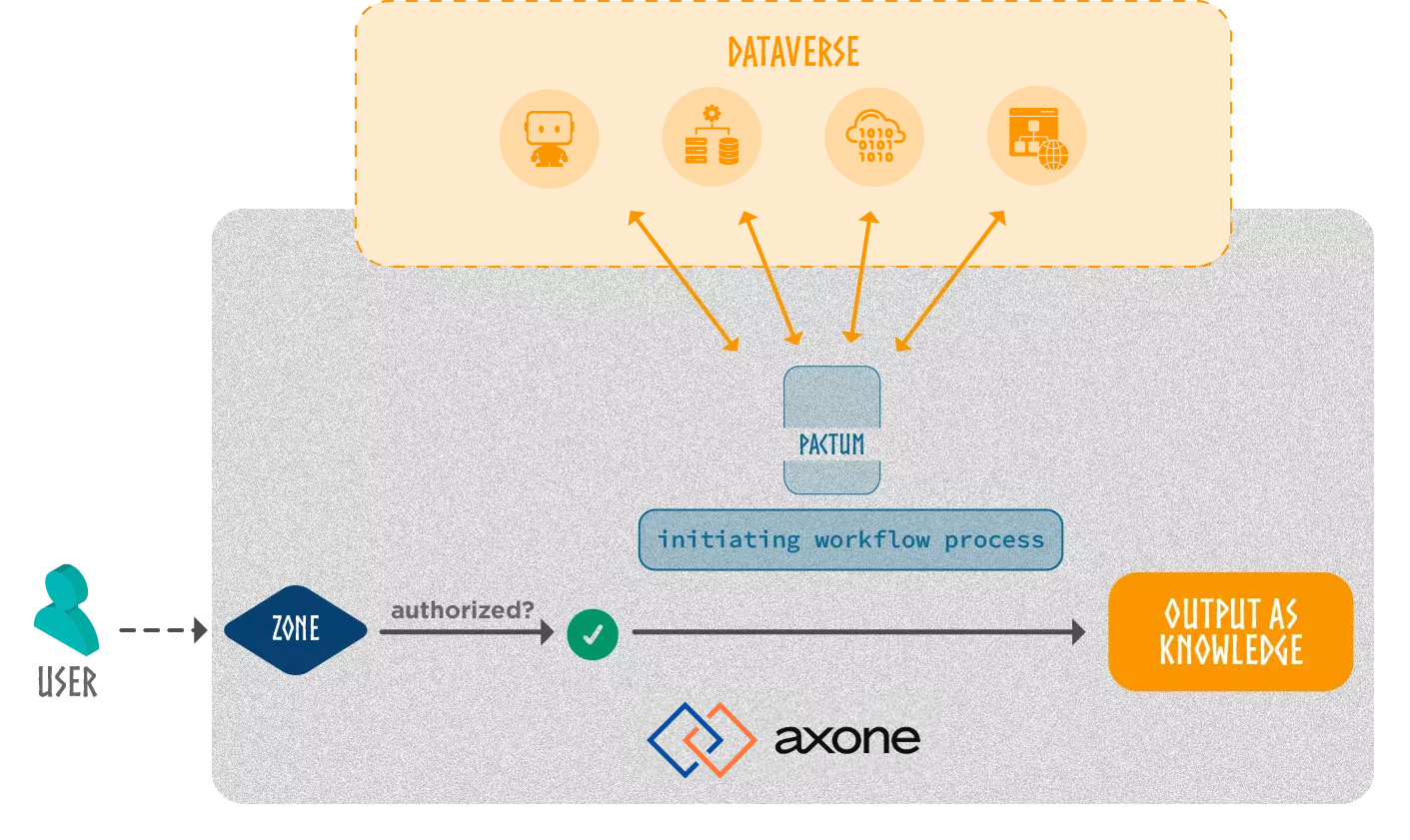
When an Identity wishes to engage a workflow within a zone, a service execution agreement as a Pactum smart contract will be established among the involved participants.
- This agreement verifies the alignment of governance rules of the zone and the digital resources involved in the execution and also checks the conformity of all rules within the entire execution context. This context includes the resources and the zone, as well as the user who initiated the workflow.
- Pactum then oversees the entire execution flow of all the resources.
- Lastly, the Pactum smart contract is able to apply retribution rules, ensuring distribution of rewards or compensation in accordance with defined retribution rules. Concretely, Pactum acts as a decentralized regulator coordinating the orchestration of digital resources and managing cases of error.
Turning Workflow Outputs into Actionable Knowledge
Once a workflow is completed, the information gained needs to be put to use. Applications can leverage this new knowledge to improve their services.
For example, let's say a professional in healthcare uses the Axone protocol to combine various resources in a workflow. The output might be a comprehensive patient health report. This information can then be used by a healthcare application to provide more personalized care recommendations to patients.
For more detailed information on the roles and various use-cases, refer to the Roles and Use Cases pages respectively.