Use case: AI Factory
The rapid development of AI models redefines the boundaries of what is possible in many fields. The ability to use existing open-source models or create one's own AI models to meet specific needs is becoming accessible to everyone.
The swift adoption by users of applications such as ChatGPT has catalyzed innovations in fundamental model architectures and other techniques. Today, many small and medium-sized technology companies, individuals, and researchers are working on new ML models or improving existing ones.
However, as is often the case in the Web2 domain, research and knowledge are not shared, evolving in silos and hindering innovation. The trade-off between risks related to trust, security, and costs versus incentives is not aligned. In this context, Axone provides an ideal solution with an open, decentralized, and interoperable infrastructure to simplify the coordination of AI resources and address fundamental misalignment in resource sharing.
Within the Dataverse, providers can share any resources under any conditions by enabling new means of coordinating and collaborating to develop collective intelligence, enhance existing solutions, and unlock new synergies.
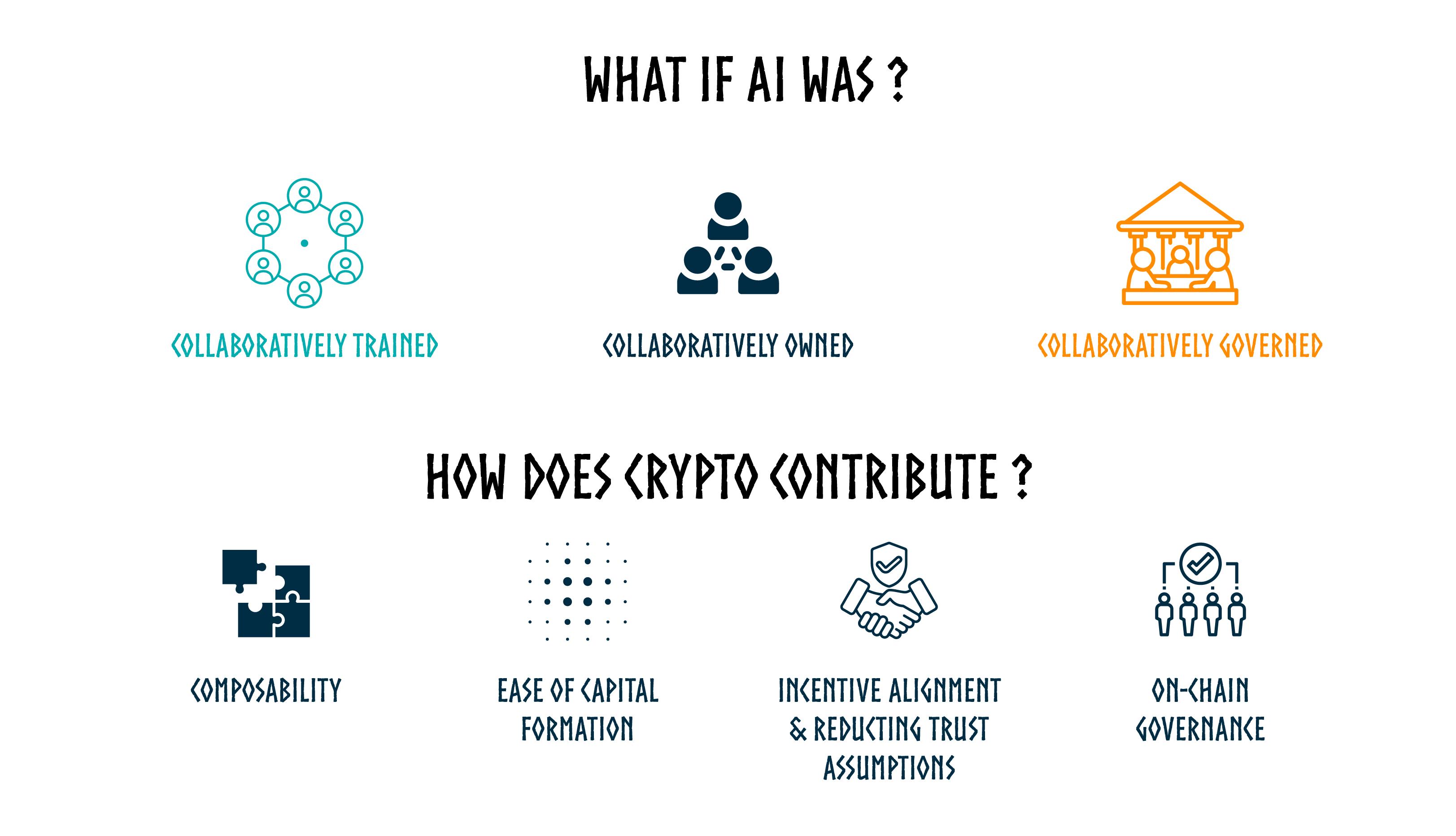
Let's delve into the AI landscape and understand why Axone is a cutting-edge solution to support AI development with an open, scalable approach.
AI Factory: Decentralized Framework for collaboratively trained and governed models
What is it?
The AI factory is a decentralized framework where anyone can collaborate and govern models, datasets, and applications. It enables the creation of a zone where different identities can coordinate around blockchain-based governance rules enforced on-chain to train a model using the wealth of resources and services from the Dataverse.
AI Factory is a set of :
- Rules & governance templates : data requirements definitions, contribution quantification, token factory for DAO's
- Open-source algorithms ready to be trained and tailored services/workflows
- Integrations and connectors
What are the benefits?
Resilient Service-Level Agreements: Axone offers robust SLAs by ensuring the integrity of computation and storage, upholding adherence to consent rules (including privacy and retribution considerations), demonstrating censorship resistance, and maintaining a transparent data provenance.
Flexibility in Governance: Axone empowers users to shape a sustainable ecosystem of services through incentivized alignment and programmable, adaptive on-chain governance. This flexibility allows for dynamic adjustments to better suit evolving needs and ensures the longevity and adaptability of the governance framework.
Modular and Interoperable Infrastructure: Within the Dataverse, Axone leverages a diverse array of resources and services, providing users with a comprehensive selection of implementation options. This modular and interoperable approach enables seamless integration and facilitates the development of solutions tailored to diverse requirements and preferences.
Performance enhancements: Collaborative training enhances performance and precision by leveraging the specialized skills of diverse contributors. Each participant can bring expertise in specific domains, resulting in an overall improvement in AI performance. Collaborative approaches solve complex problems by combining multidisciplinary knowledge, leading to more accurate and efficient AI models.
Diversity and reducing biases: Collaborative AI Training fosters diversity in perspectives and data. By involving multiple stakeholders in the AI training process, diverse perspectives and experiences are brought to the table. This collaborative effort allows the AI to be trained on a broader set of data, reflecting various real-world situations. The diversity in training data contributes to making models more robust and generalized, thereby reducing potential biases associated with limited datasets.
How does it work?
In practical terms, AI Factory is represented by three key aspects:
- On-chain Rules and Governance Templates
- All Referenced Resources and Services in the Dataverse Accepted within the zone's Scope
- Integrated Tools and connectors to interconnect with users' existing workflows.
Rules & Governance Templates
Defined as a set of rules, these on-chain governance templates establish the boundaries and operational scope of the zone. They provide a structured framework that outlines the permissible actions and existence parameters within the zone.
The zone creator can create his own template or reuse an existing one to deploy a framework tailored to quickly specific needs.
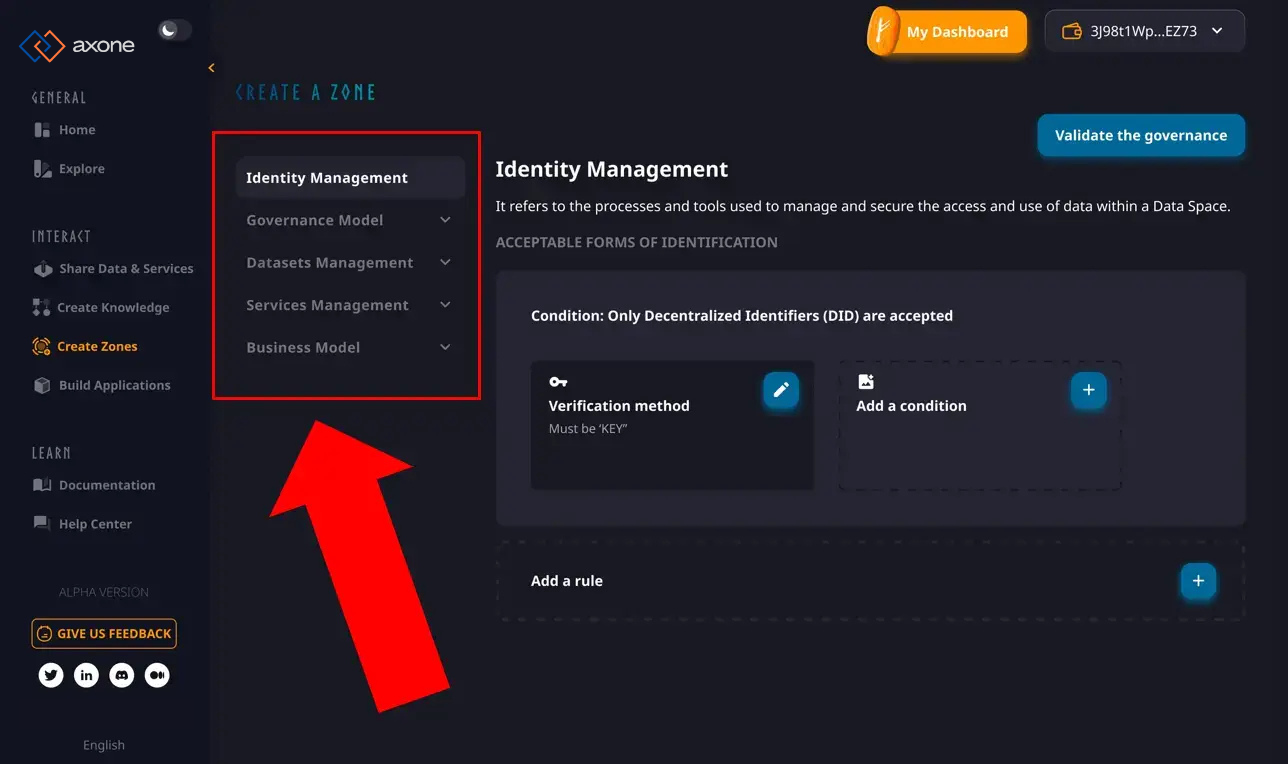
Identity Management: This refers to the various authentication methods used to manage access to the zone. It can range from key-based systems Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) services like Cheqd to more conventional Single Sign-On (SSO) methods like Sign-in with Google. The choice may depend on the desired contributor engagement type or the disclosed information's granularity.
Governance Model: Determines how governance is exercised and expressed, ranging from a model with a single authority to a multi-sig or a DAO around a token model. All governance rules can be defined, allowing for a highly customizable governance structure.
Resource Management: Define the conditions under which digital resources can be considered within the scope of an activity involving acting entities. Numerous rules can be expressed regarding the properties of the digital resources established by their metadata. Rules related to metadata requirements, format compatibility, size limitations, ownership and intellectual property rights, and quality assurance may be included.
Business Model: The business model of the zone defines how contributions are quantified and how contributors are rewarded. This can range from a simple one-time payment for access to more complex business logic aiming to create an AI Factory with specific services that require a fair and sustainable compensation system for each contributor.
Once all defined, the zone is registered with a transaction to enforce the rules on-chain.
Resources and Services allowed and compatible
Once the governance framework is defined and live on-chain, the protocol can determine the resources that are usable within the newly created AI Factory zone based on two criteria
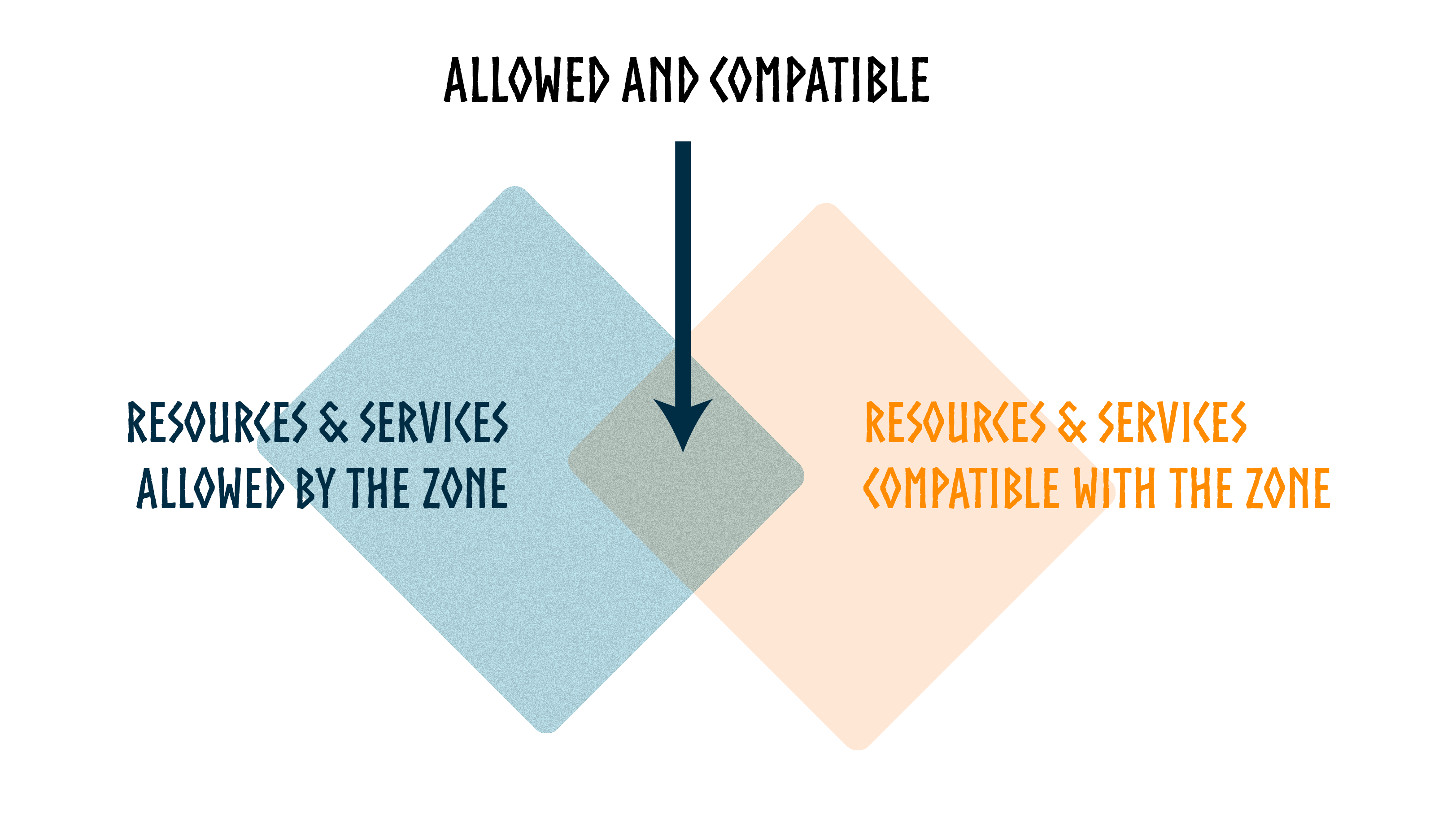
All Resources and Services allowed by the zone: The governance rules of the zone help determine, within the set of resources referenced in the Dataverse, which ones can be used within the scope of this zone. All Dataverse resources adhering to these rules are allowed by the zone.
All Resources and Services compatible with the zone: Resource Consent defines the conditions for including a resource in an activity involving entities operating within a zone. While the zone rules specify the regulations from the perspective of the zone, the consent represents the rules from the perspective of the Resource. It serves as the expression of the resource owner's considerations regarding the terms of use for the Resource, providing guidelines for its proper use within the Dataverse. Rules may include aspects such as the business model, zone licenses or labels, and regulations about any credentials, such as identity, reputation, qualification, or token-related credentials.
All Dataverse resources adhering to these rules are compatible with the zone.
Understanding the unique relationship between the consent of resources and the zone rules is essential. The licenses and zone rules must be compatible, as the powers of a zone recognizing a resource as being included and thus compatible with its operation require reciprocal confirmation of compliance from the helpful resource. Read the technical documentation about Governance and the hierarchy of norms
Essential Types of Resources and Services:
- Training Dataset: Encompasses various forms of data and information expressed, carried, and stored in different formats (structured or unstructured data, data streams, etc.).
- AI Model: Ranges from foundational models to specialized models, from LLM to SLM, with the choice typically depending on the type of task for which the model is to be trained. Any kind of model may be provided.
- Storage Infrastructure Provider: Supports all storage options, ranging from local storage to cloud storage solutions provided by significant companies like Dropbox or AnyDrive. Additionally, decentralized storage networks such as Interplanetary File System (IPFS), Jackal, or Arweave can be connected to the Dataverse.
- Compute Infrastructure Provider: The Dataverse is adaptable to various computation options, including APIs with their own computational resources, cloud services by commercial entities, or decentralized computing resources. This flexibility accommodates different types of computational tasks and workloads. Relevant general-purpose compute networks like Akash can be easily referenced in the protocol. Depending on the type of model to be trained, different kinds of components may be necessary, such as CPU, Gaming GPU, or AI-specialized GPU.
- Orchestration Service: This crucial service orchestrates the invocations of other services. Notably, a decentralized mechanism is in place to ensure the correct instance of the appropriate type is executed, given the potential for multiple instances of the service and several kinds of orchestration services.
Integration and Connectors:
- APIs and Connectors: APIs provide a standardized interface for accessing and communicating with a service, while connectors are components that facilitate the connection between two distinct systems by overcoming potential differences in their protocols and communication methods. They are crucial for ensuring the connection between different services and the orchestrator.
- Front-end Interface: It serves as the user-friendly entry point for interacting with the zone. A front-end interface acts as a crucial bridge, enabling effective communication and interaction between users and the decentralized framework.
As the Dataverse continues to expand, numerous interfaces and APIs will become available, created by the community or external contributors to facilitate accessibility and entry points.
Unlock New Synergies with AI Factory
It is crucial to emphasize that Axone does not aim to reconstruct each infrastructure component necessary for developing and enhancing the AI Factory individually.
Axone's mission is to provide a decentralized orchestration layer for off-chain resources. This means that Axone seeks not to rebuild each infrastructure component one by one for the development and improvement of the AI Factory.
The goal is to create the most modular and expressive orchestration framework to enable interconnection between cutting-edge services.
Let's consider projects like Akash, which provides an open marketplace for general-purpose computation, or Jackal, offering various decentralized storage solutions. We believe that their solutions are highly relevant in their respective domains. Our role is to facilitate communication and orchestration between these technologies and provide them with a more expansive governance framework.
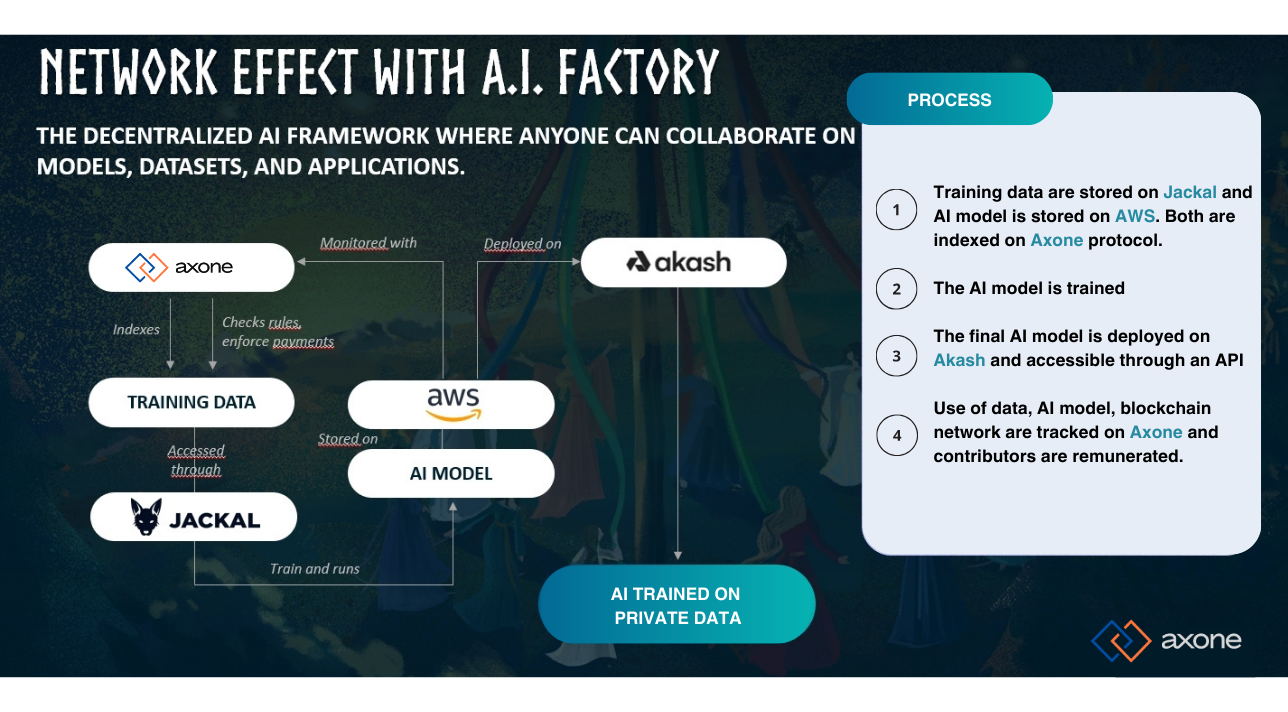
We believe that the AI Factory, by offering a highly customizable Training-as-a-Service, opens new perspectives in the field of AI development. This approach significantly expands the training capabilities of models while ensuring a diversity of applications to address. With its flexibility and advanced customization, the AI Factory becomes a powerful lever to meet specific and complex needs, providing an unprecedented common space for collaborative training and decentralized governance of AI models. This technological advancement represents a major step toward the creation of a dynamic and diversified AI training community, ready to tackle the most challenging issues in the field of AI.
Beyond the AI Factory
The AI Factory serves as the initial milestone for collaborative model training. With ongoing advancements in the field of AI, we foresee industry diversification and increasing specialization of applications. To significantly expand the capabilities of AI services within the Dataverse, it is not surprising to envision the emergence of numerous zones compatible with the AI Factory. These zones would offer complementary services to enhance the quality of model creation, training, and inference. As the Dataverse grows and diversifies, it becomes the ideal playground for crafting highly personalized AI models. Thanks to crypto-economics, numerous implementations of open-source tech can discover their business models, thereby contributing to the enrichment of innovation and knowledge within the Dataverse.
Here is a non-exhaustive list of projects we anticipate rapidly emerging within the Dataverse, contributing to innovation in AI:
Inference Marketplace Zone
This zone acts as a marketplace where contributors can offer and access AI inference services. Contributors collaborate to provide efficient and specialized inference capabilities, creating a dynamic ecosystem for deploying and utilizing AI models in real-world scenarios. On-chain rules define the terms of service and ensure transparent transactions within the marketplace.
Aggregator of AI Inference Zone
It serves as an aggregator for AI inference services, allowing contributors to pool resources and offer collective solutions. The zone facilitates collaboration to optimize and aggregate inference results from multiple models. On-chain rules govern the aggregation process, ensuring fair contributions and quality output.
Specialized Infrastructure Provider Zone
Zone Purpose: addresses specific infrastructure requirements by providing a decentralized marketplace for contributors to access various compute chipsets, whether heterogeneous or homogeneous, tailored to specific AI model needs.
Fine-Tuning Zone
This Zone is designed for fine-tuning AI models to enhance their performance. Contributors collaborate to make nuanced adjustments, iterating on model parameters and hyperparameters to achieve optimal results. On-chain rules define the fine-tuning parameters and ensure the traceability of refinements made to the models. Most relevant fine-tuning algorithms, such as Grid Search, Random Search, and Bayesian Optimization, may easily be implemented as a service into the Dataverse.
Edge Computing Infrastructure Zone
This zone specializes in providing resources optimized for edge computing scenarios. Contributors can access infrastructure solutions designed for deploying AI models at the network edge, reducing latency and enhancing real-time processing. Edge computing chipsets and configurations allow contributors to meet the unique demands of applications requiring fast and decentralized AI processing on the edge. The on-chain rules of this zone ensure seamless compatibility and provide clear usage conditions for contributors leveraging edge computing infrastructure.
Data Pre-Processing Zone
This Zone focuses on preparing data for AI model training through various pre-processing tasks such as data ingestion, cleaning, and outlier detection. Contributors collaborate to ensure that datasets are well-structured and cleansed, addressing data quality and integrity challenges.
Privacy-Preserving Data Labeling Service
Collaborators can use privacy-preserving data labeling tools that allow for data annotation without exposing personally identifiable information, contributing to developing privacy-conscious AI models.
Secure Multiparty Computation Services Zone
Zone Purpose: is dedicated to providing Secure Multiparty Computation (SMPC) services, allowing contributors to perform computations on encrypted data without exposing the raw information. This specialized zone enhances privacy during collaborative model development, ensuring that sensitive data remains confidential throughout the computation processes.
Zero-Knowledge Machine Learning Zone
Zone Purpose: ZKML focuses on zero-knowledge machine learning techniques, providing a collaborative space for contributors to develop privacy-preserving AI models. Contributors collaborate to integrate advanced privacy features using zero-knowledge proofs. On-chain rules define the privacy standards and usage conditions within the zone.
Monitoring Zone
This zone specializes in real-time monitoring of AI model performance in training or production. Contributors can access advanced monitoring tools that alert them to deviations or performance degradation. On-chain rules define monitoring parameters and ensure responsiveness to issues.
Simulation Tools Zone
Enables the testing and validation of models in simulated environments before deployment in production. Contributors collaborate to create realistic simulations, ensuring the robustness of models. On-chain rules define the conditions for using simulation tools.
Model Explainability Tools Zone
It focuses on enhancing the transparency of AI models by providing explanations for decision-making processes. Contributors collaborate to make models more understandable, reinforcing user trust. On-chain rules ensure the quality and objectivity of generated explanations.
Dimensionality Reduction Tools Zone
This zone can facilitate the management of complex datasets by reducing their dimensionality. Contributors collaborate to apply reduction techniques while preserving essential information.